Remediation Requests
This article details the different remediation requests you can create in the Brinqa Platform and the request workflow.
What are remediation requests?
In vulnerability management, an exception is a decision to deviate from the standard remediation process for a known vulnerability. Exceptions are typically granted when the vulnerability is a false positive, implementing the mitigation needs more time, or remediation of the vulnerability is deemed infeasible.
As you adopt the Brinqa Platform to prioritize vulnerabilities and accelerate the remediation process, you can create remediation requests to handle exceptions. You can select the relevant findings and create requests for time-based extensions, false positives, or risk acceptance. The following table provides more details on each type of request:
| Request Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Exception | This request asks for a time-based extension on the selected findings. You need to specify the extension date by which the findings must be resolved. |
| False positive | This request nominates the selected findings to be false positives. |
| Remediation validation | This request seeks to mark a finding as fixed. For example, if a pen test doesn't provide a status, this request can help provide one. |
| Risk acceptance | This request accepts the risks associated with the selected findings. |
The remediation request workflow
In the Brinqa Platform, a remediation request workflow involves a submitter and a reviewer. Submitters can create requests or submit requests created by other authorized personnel. Reviewers evaluate the selected findings and approve or reject the requests. The designated users receive notifications when they need to perform an action and they must provide a justification for each action they take. All activities in the workflow are audited for compliance purposes. The following diagram illustrates the process:
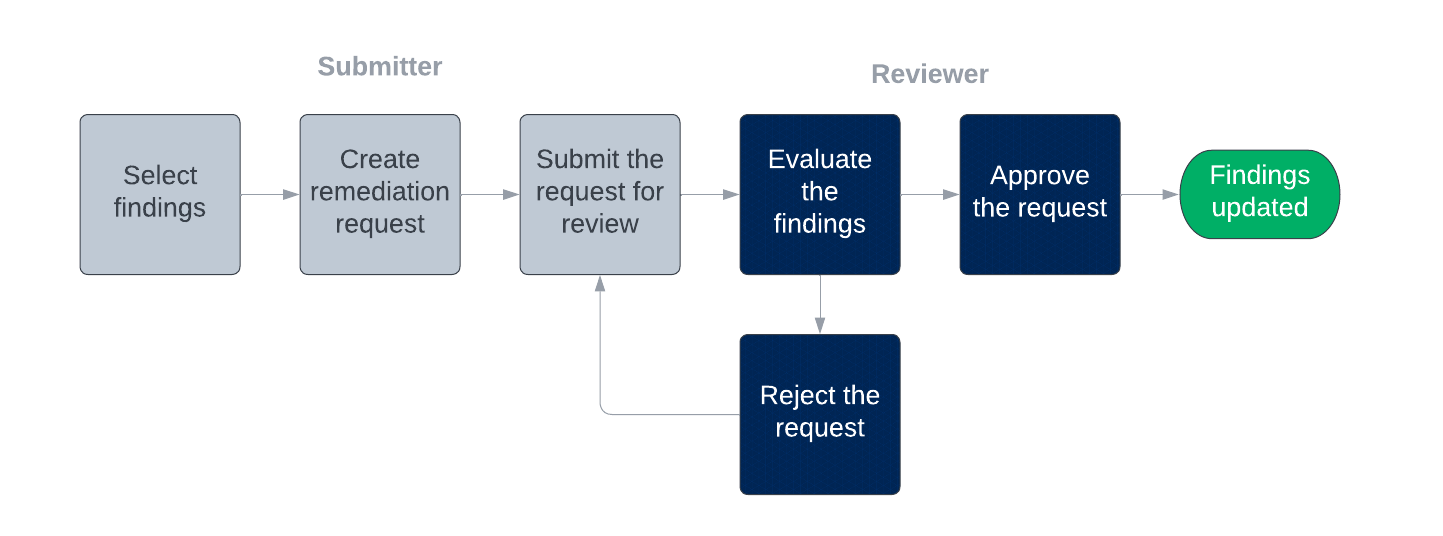
Figure 1. The remediation request workflow
Submitters and Reviewers must be able to view the findings included in a remediation request. By default, only system administrators can view all the findings, but you can provide users of the Risk analyst role access to the relevant findings by creating risk owners and remediation owners clusters, respectively.
Risk owners cannot delegate approval of remediation requests to another risk owner.
Create remediation requests
There are two methods to create remediation requests:
-
Select the findings manually. The list of findings in the request does not change if you select the findings manually.
-
Use automations. The list of findings in the request updates automatically each time the automation runs.
The benefit of using automations is that you can set the automation to run at a schedule or as part of the data orchestration, so that the Brinqa Query Language (BQL) query you specify to identify the findings is executed every time the automation runs, keeping the findings in the request dynamic and up-to-date.
Create a request manually
To create a request manually, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to All findings or any findings page.
-
Click the checkbox next to the findings you want to include in the request.
-
Click the Select an action dropdown to choose the request you want to create.
The Select an action option doesn't display until you select at least one finding.
-
A request form displays with the following fields:
-
Name: Enter a name for your request.
-
Description: (Option) Provide a description for the request.
-
Justification: Provide an explanation for the request.
-
Evidence: Provide evidence to support your explanation.
-
Exception request date: Select the extension or expiration date for the exception. This field is only available in exception requests.
-
Submitter: Select the user designated to be the submitter. The user must possess the Risk analyst role, and you can restrict their access to specific findings by assigning them to a risk owners cluster.
-
Reviewer: Select the user designated to be the reviewer. The user must possess the Risk analyst role, and you can restrict their access to specific findings by assigning them to a remediation owners cluster.
-
Continuous finding reevaluation: Click to enable this option and automatically update the findings in the request based on the BQL query. Click again to disable it and keep the findings static.
infoWhen you select findings manually from a list, the platform generates a static BQL query such as:
FIND Vulnerability AS v WHERE v.id IN [1983179460715253762, 1983179460715253760]. This query is static because the IDs don't change. However, if you create the request using a BQL query, such asFIND Vulnerability WHERE riskRating = "Critical", the set of vulnerabilities may change over time.When you enable Continuous finding reevaluation with a non-static query, the query is reevaluated each time orchestration runs or when manually executed as an action. The findings in the request are then updated based on the current results of the query. The request includes a Findings last evaluated date that updates each time the query is evaluated and findings are refreshed.
-
-
Click Submit.
When creating a remediation request, you may encounter the following error message:
"A request already exists with the name 'xxxxx'. Choose a different name."
This error occurs when . To proceed, ensure that only findings not already tied to an existing request are selected for the new exception request.
Create a request through automation
To create a request through automation, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Automation.
-
Click Create.
-
Provide a title and description for the automation.
-
Type a BQL query to limit your findings.
-
Click Test to ensure that your query is valid and returns the expected data.
-
In Actions, select the request you want to create and fill out the following fields:
-
Name: Enter a name for your request.
-
Description: (Optional) Provide a description for the request.
-
Justification: Provide an explanation for the request.
-
Evidence: Provide evidence to support your explanation.
-
Exception request date: Select the extension or expiration date for the exception. This field is only available in exception requests.
-
Submitter: Select the user designated to be the submitter. The user must possess the Risk analyst role, and you can restrict their access to specific findings by assigning them to a risk owners cluster.
-
Reviewer: Select the user designated to be the reviewer. The user must possess the Risk analyst role, and you can restrict their access to specific findings by assigning them to a remediation owners cluster.
-
Continuous finding reevaluation: Click to enable this option and automatically update the findings in the request based on the BQL query. Click again to disable it and keep the findings static.
infoThe BQL query you specify in the automation can be static or non-static. A static query uses fixed values that don't change, such as:
FIND Vulnerability AS v WHERE v.id IN [1983179460715253762, 1983179460715253760]. A non-static query uses criteria that may return different results over time, such asFIND Vulnerability WHERE riskRating = "Critical".When you enable Continuous finding reevaluation with a non-static query, the query is reevaluated each time orchestration runs or when manually executed as an action. The findings in the request are then updated based on the current results of the query. The request includes a Findings last evaluated date that updates each time the query is evaluated and findings are refreshed.
-
-
In Run, select a method to run the automation:
-
Manual: Select this option if you don't want any changes to the list of findings in the request. You can manually run the automation once.
-
Schedule: Select a schedule from the dropdown.
-
Orchestration: Select After consolidation from the dropdown.
If you want the list to be updated automatically, select a schedule for the automation to run or set it to run as part of your data orchestration.
-
-
Click Create.
The Automation page reloads and your new automation appears in the list of available automations.
Review remediation requests
After a request has been created, submitters can revise the requests before submitting. The reviewer specified in the request receives an email after a request has been submitted. Reviewers then evaluate the findings and offer an approval or rejection. Submitters have the option to re-submit a request after it has been rejected. Submitters can also cancel requests. If the request has already been approved when it is canceled, the findings are removed from the request and their status are reverted.
Navigate to Remediation > Requests to view the requests. Users can only see the requests that they have access to, including the following:
-
Requests that you have created
-
Requests on findings that you can view
-
Requests of which you are a reviewer
Hold the pointer over the request and click Details to launch the detailed view of the request. The designated owners can perform actions through the buttons on the upper-right corner. Click the Comments & Attachments tab to view the justification (as comments) for each action and the Activity tab for the timeline.
Add or remove findings from a request
Regardless of how the remediation request is created, manually or through automation, you can add or remove findings afterwards if needed. A separate tab displays the findings that have been added or removed.
To add more findings to a request, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to All findings or any findings page.
-
Select the checkbox next to the findings you want to add to the request.
-
Click the Select an action dropdown and choose the request type.
The Select an action option doesn't display until you select at least one finding.
-
In Add findings to an existing request, select the request to which you want to add the findings.
noteOnly requests with New, Rejected, or Expired status can accept additional findings.
-
Click Submit.
-
After the process has successfuly completed, go to the request's Details page and click the ADHOC added tab to verify that the findings match your selection.
To remove findings from a request, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the Details page of the request.
-
Select the checkbox next to the findings you want to remove.
-
Click the Select an action dropdown and select Remove findings from a request.
The Select an action option doesn't display until you select at least one finding.
-
Click Submit when prompted.
-
After the process has successfuly completed, click the ADHOC removed tab to verify that the findings match your selection. If the list isn't updated, click the refresh button.
Push requests to external sources
You can push requests created in Brinqa Platform to external Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) systems, such as AuditBoard, MetricStream, or ServiceNow GRC. This section describes how to push requests to ServiceNow GRC.
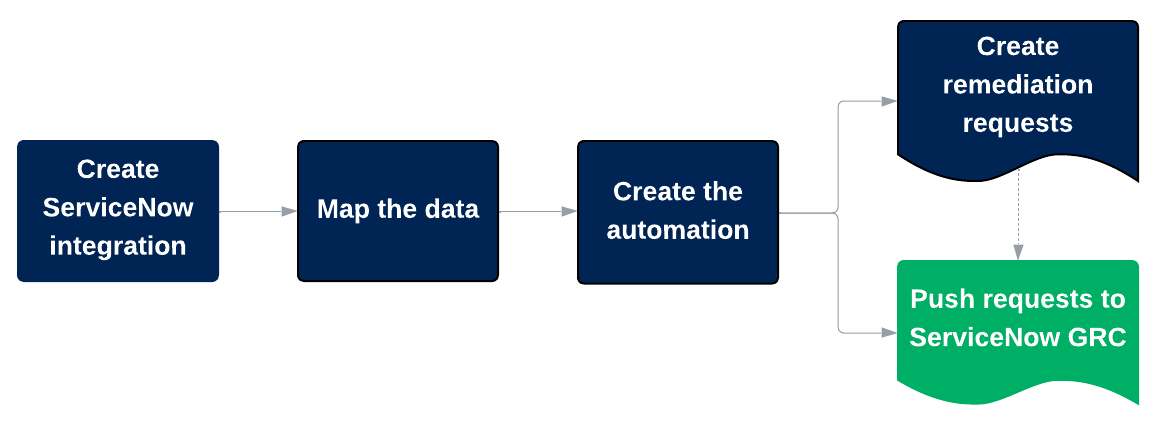
Create data integration for ServiceNow GRC
Before you can push requests to your organization's ServiceNow GRC system, you need to install and use the ServiceNow connector in a data integration. Only users with the System Administrator role can create data integrations. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Integrations > Connectors.
-
Locate the ServiceNow connector and click Install.
-
Click Use. The Create data integration screen displays.
-
Fill out the General information.
-
Title: Provide a title for the data integration. For example, "ServiceNow GRC."
-
Connector: The Connector field is filled in with the ServiceNow connector.
-
Server: The server to process the data integration. Local Server is selected by default for cloud data sources. You can also create your own data servers for on-premises data sources.
infoIn Brinqa Platform version 12, a Version field appears between Connector and Server, allowing you to select the connector version. Additionally, the default server is named Cloud Server instead of Local Server.
-
Description: Provide a description for the data integration. For example, "ServiceNow GRC data integration to push Brinqa remediation requests to ServiceNow GRC issues."
-
-
Fill out the Connection information for the ServiceNow connector.
-
ServiceNow URL: Your organization's ServiceNow Server URL. The default format is
https://<ServiceNowServerName>.service-now.com/. -
Username and Password: The username and password associated with the ServiceNow user account, which must have permissions to access ServiceNow GRC tables and return data. For information about how to create a ServiceNow user with the necessary roles, see Create a ServiceNow user and Assign the required roles and permissions.
-
Client ID and Client secret: The client ID and client secret for OAuth2 access to ServiceNow. When specified, the ServiceNow connector uses OAuth2 authorization. If not specified, the ServiceNow connector reverts to basic authorization using the ServiceNow username and password provided. For information about how to generate these credentials, see Obtain the client ID and client secret for 0Auth2 authentication.
-
Additional tables: Type sn_grc_issue. The
sn_grc_issuetable in ServiceNow GRC is used to track governance, risk, and compliance issues. This table is mapped to the Request data models in the Brinqa Platform, ensuring that your remediation requests are pushed to ServiceNow GRC as issues. -
Leave Page size, Parallel requests, and Maximum retries as is.
-
Use cached schema: Select this option to allow Brinqa to use a previously stored version of the ServiceNow schema when connecting to ServiceNow. This can speed up the connection process and reduce the load on ServiceNow.
-
-
Click Next.
-
For Types, choose Issue. This is the ServiceNow GRC
sn_grc_issuetable you added earlier in the steps. -
For Sync Interval, choose how far back you want to sync your data. By default, the beginning of time is selected, which means when the request is created in your Brinqa Platform. You can leave this field as is.
-
For Data lifecycle, specify the number of days of inactivity after which the data retrieved by the ServiceNow integration is marked as inactive and then removed from the Brinqa Platform. The default is 30 days. See Data lifecycle management for additional information.
-
Click Create.
If you have completed the fields correctly, the page reloads and you should see the ServiceNow data integration listed. If you do not see it, click Refresh .
The ServiceNow data integration syncs when the data orchestration runs.
Configure data mapping for ServiceNow GRC
After creating the ServiceNow data integration, you need to create a data mapping to sync the requests created in the Brinqa Platform to ServiceNow GRC issues. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Integrations > Sources.
-
Hold your pointer over the ServiceNow data integration, click the kebab (three vertical dots) menu, and then click Mappings.
-
Click Create and fill in the following fields:
-
Title: Provide a title for the data mapping. For example, "Remediation requests to ServiceNow GRC issues."
-
Source: The data model containing the data you want to push. Select the appropriate request type (e.g., Exception request, False positive request, Risk acceptance request, or Remediation validation request).
-
Target: The ServiceNow table specified for Types in the ServiceNow data integration. Click the dropdown and select Issue.
-
Active: Select Active if not already selected.
-
-
Click Map attributes. Mapping source attributes to targets lets you match aspects of the Brinqa requests that are pushed to ServiceNow GRC issues.
-
Click the desired source attribute, use Search if needed, and then click the target attribute. A line displays linking the mapped attributes.
For the best compatibility and consistency between requests created in the Brinqa Platform and ServiceNow GRC, map the following attributes as appropriate for your organization's needs:
Source Target Name Short description Description Description Due date Due date Status Status noteThe exact field mappings may vary depending on your ServiceNow GRC configuration and customizations. Consult with your ServiceNow GRC administrator to determine the appropriate field mappings for your organization.
-
Click Preview to ensure that the source attributes and targets align.
-
Click Create.
Create an automation
To push requests from the Brinqa Platform to ServiceNow GRC, you must create an automation. Only users with the Configurator or System Administrator role can create automations. To create an automation that generates exception requests for critical vulnerabilities and pushes them to ServiceNow GRC, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Automation.
-
Click Create and fill in the following fields:
-
Title: Provide a title for the automation. For example, type "ServiceNow GRC Sync."
-
Description: Provide a description for the automation. For example, type "Push exception requests created in Brinqa to ServiceNow GRC."
-
-
Type the following Brinqa Query Language (BQL) query to retrieve all critical vulnerabilities in your data:
FIND Vulnerability AS v WHERE v.riskRating = "Critical"warningAvoid using "Finding" in the BQL query. Instead, choose a data model that extends the "Finding" model, such as Alert, Manual finding, Pentest finding, Violation, Vulnerability, etc. If you create an automation for generating tickets and use "Finding" in the BQL query, it will not work as intended and will result in tickets being created with empty counts.
-
Click Test to ensure your query is valid and returns data.
-
In Actions, select the type of requests you want to create. In this example, select Create exception request and fill out the form. See Create a request through automation for assistance.
-
Click Add action and select Push exception requests. Additional options display.
- For Data integration mapping, select the mapping created for ServiceNow GRC in the Configure data mapping for ServiceNow GRC section.
-
In Run, select a method to run the automation.
-
Manual: Manually launch the automation from the Automation page.
-
Schedule: Specify a schedule for the automation to run (for example, once per day at a specified time).
-
Orchestration: Set the automation to run as part of the data orchestration.
-
-
Click Create.
Launch the automation
After creating the automation, wait for it to run at its scheduled time or launch it manually. To run the automation manually, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Automation.
-
Hold your pointer over the ServiceNow GRC automation and click Run.
-
Click Confirm when prompted.
-
After a successful run, navigate to Remediation > Exception.
-
Search for the request by typing its name.
-
Hold your pointer over the request and click Details to view the details.
-
Log in to your ServiceNow GRC system and verify that the requests were received from the Brinqa Platform as GRC issues.
Troubleshooting
If the automation run fails, you can view information about what caused the failure. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Automation and select the automation for which you want to view logs.
-
Copy the Transaction ID of the failed automation run.
-
Navigate to Administration > System > Logs.
-
Paste the Transaction ID into the search bar and press Enter or Return.
-
Click the link in the Message column to see what caused the automation to fail. The error message is included in the Detail section.
Common questions about remediation requests
What happens to the associated findings when the request is approved?
The behavior varies based on the type of request. Expand the sections below to find out the specifics:
Exception
When an exception request is approved, the status of the associated findings change as follows:
- The status of active findings become "Risk temporarily accepted".
- The status of fixed findings remain unchanged.
Their Extended due date attribute is set to the date specified in the exception request and the compliance status is evaluated against the extended due date instead.
If a finding is resolved before the exception expires, the status of the finding changes to "Fixed".
Findings with the risk-temporarily-accepted status still count as active risks for dashboards and tickets.
False positive
When a false positive request is approved, the status of the associated findings change to "False positive", and their compliance status is always "No SLA required”
Findings with the false-positive status do not count as active risks for dashboards or tickets. This may affect the risk score of the host that the finding resides on.
Remediation validation
When a remediation validation request is approved, the status of the associated findings change to "Fixed", and their compliance status is evaluated against the due date. This may affect the risk score of the host that the finding resides on.
Risk acceptance
When a risk acceptance request is approved, the status of the associated findings change to "Risk accepted", and their compliance status is always "No SLA required”.
Findings with the risk-accepted status still count as active risks for dashboards, but they cannot generate tickets because they are considered closed. This may affect the risk score of the host that the finding resides on.
Approving a false positive, remediation validation, or risk acceptance request may downgrade a host's risk level. This downgrade occurs because a host's risk score is based on the highest risk score of its open findings. After request approval, findings marked as "False positive", "Fixed", or "Risk accepted" are considered "Closed" and no longer contribute to the host's risk score. The host's risk score would be adjusted to reflect the next highest risk score among its open findings.
What happens to the associated findings when the request is expired?
The behavior varies based on the type of request. Expand the sections below to find out the specifics:
Exception
If the associated findings are not resolved by the extended due date, and the exception request has been approved, the request becomes expired and the status of the findings are reverted. The extended due date entries are removed, and the compliance status is re-evaluated against the original due date. You must re-submit the request if it still applies.
Exception requests that haven't been approved do not expire, even if the extended due date specified in the request has elapsed.
False positive
False positive requests do not expire but they can be canceled, whereupon the findings' status are reverted.
Remediation validation
Remediation validation requests do not expire but they can be canceled, whereupon the findings' status are reverted.
Risk acceptance
Risk acceptance requests do not expire but they can be canceled, whereupon the findings' status are reverted.
What happens to the associated findings when the request is reopened?
If needed, you may reopen expired exception requests, whereupon the status of the associated findings are reverted. The requests can then be submitted for review and go through the remediation request workflow again.
Approved requests can be canceled, but not reopened.
How are canceled and modified automation requests handled?
When a request created from an automation is canceled, the workflow restarts and continues processing the eligible findings that match the criteria of the BQL query. If the BQL query for an automation associated with a remediation request is modified, the request continues to use the original query. To apply a new query, you must create a new remediation request.
How do manual and automated requests interact?
If a finding associated with a manual exception request matches the criteria of an automation that generates exception requests, that finding is added into the automated request upon the next run of the automation and retains its status from the manual request. If the finding is in multiple approved requests, there's a hierarchy of which status it will give. The order of precedence is as follows: false positive > remediation validation > risk acceptance > risk temporarily accepted.
How are new findings handled in automated exception requests?
The new finding(s) is added to the existing request as long as the automation associated with that request runs again (i.e., it's set to run on a schedule or as part of orchestration). If that automation isn't run, nothing happens with that finding.
Can you modify the exception date for an approved exception request?
No, the exception date cannot be modified after an exception request has been approved. The exception either expires, and you can change the date during the review process, or you can cancel the exception and create a new request.
Can you submit and approve risk acceptance against risk-temporarily-accepted findings
Manual submissions and approvals of risk acceptance against risk-temporarily-accepted findings are not possible. However, this can be done through automation.