Just-in-Time Provisioning through Microsoft Entra ID
This article details the process for just-in-time (JIT) user creation and the configuration of their access permissions using Microsoft Entra ID (formerly known as Azure Active Directory or Azure AD).
Process overview
Customers who have established secure access to the Brinqa Platform through single sign-on (SSO) can leverage the users and groups information contained in the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) claims. In other words, when users log in for the first time, relevant roles are assigned based on the SAML claim; the users are added to the relevant ownership clusters, also based on the SAML claim. The following diagram illustrates this process:
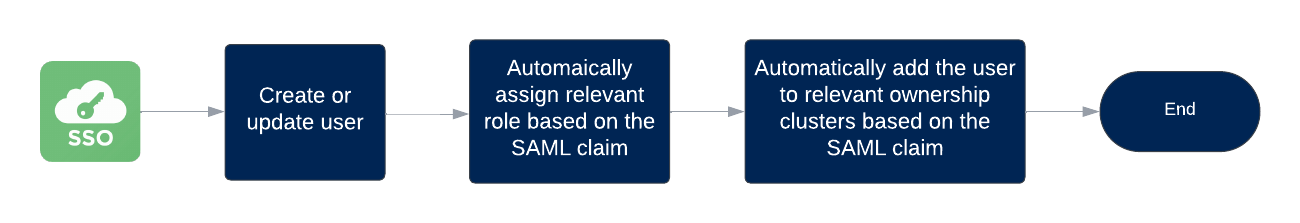
Figure 1. JIT user access provisioning process
The remainder of this article uses Microsoft Entra ID as an example to provide detailed instructions on JIT user provisioning.
Configure SSO
Before setting up JIT provisioning in Microsoft Entra ID, you must first configure single sign-on to the Brinqa Platform using Microsoft Entra ID as the Identity Provider (IdP). As a result, you would create a non-gallery enterprise application in Microsoft Entra ID to represent Brinqa. For ease of understanding, we'll refer to this application as "Brinqa app" throughout the remainder of this article.
Create a security group for the risk analyst role
Next, you must create a security group in Microsoft Entra named "Risk analyst" and populate this group with users who need access to the Brinqa Platform. As these users make their initial logins on Brinqa, the SAML claim containing this group affiliation will lead to their automatic assignment of the Risk analyst role. To ensure this process functions seamlessly, you must create the group with the exact name in Microsoft Entra, as shown in the screenshot:
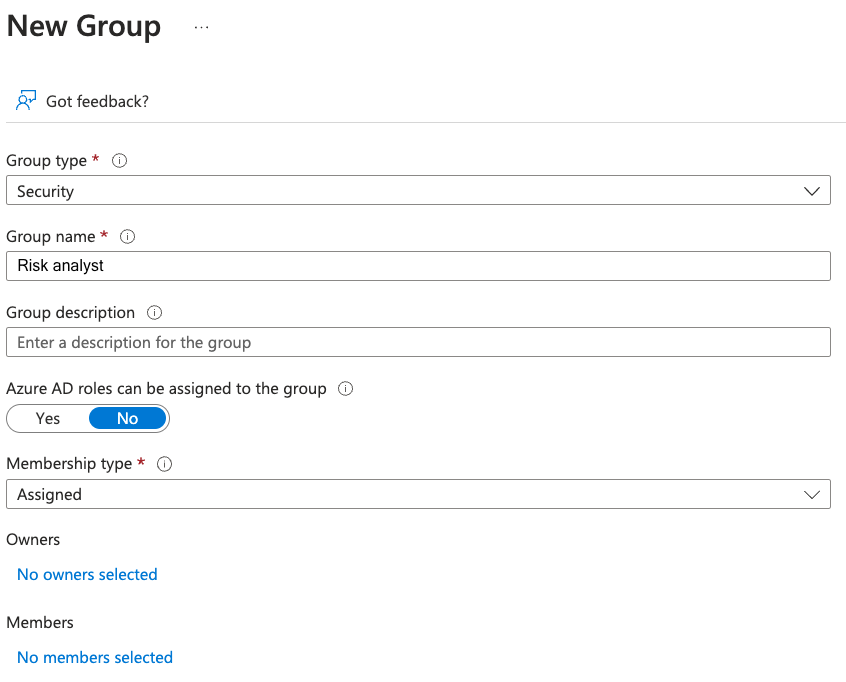
Then, add this new group to "Brinqa app", the enterprise application you've created to represent Brinqa. Refer to Microsoft documentation for instructions if needed.
You must have a Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2 license to assign groups.
Set up claims in Microsoft Entra ID
In addition, you must update "Brinqa app" to send user and group attributes in the SAML claims. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Log in to your organization's Microsoft portal as an Administrator.
-
Click Enterprise Applications and select "Brinqa app".
-
In the single sign-on configuration, locate Attributes & Claims and click Edit.
-
Click Add a group claim.
-
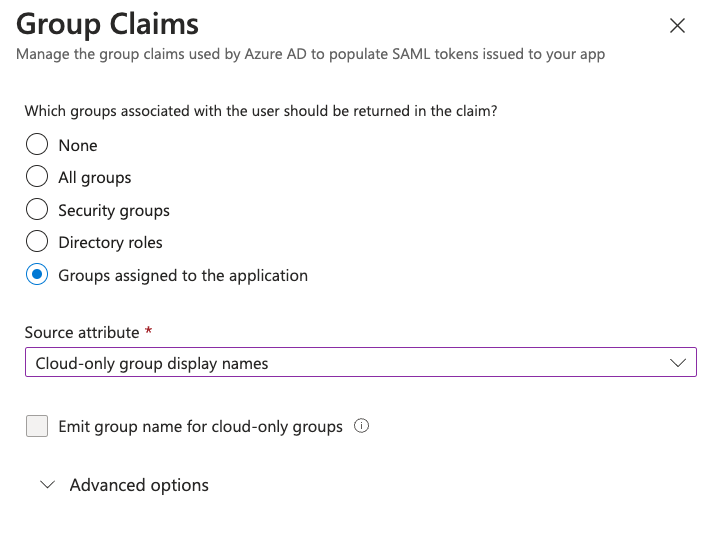
Select the options as shown in the screenshots:
Groups assigned to the application: Only export groups that have been explicitly assigned to the application and that the user is a member of.
Cloud-only group display names: Export group display names only for cloud groups.
-
Make sure that all users who access the Brinqa Platform are in the respective groups.
Create ownership clusters in Brinqa
Lastly, you must create ownership clusters in the Brinqa Platform. The purpose of the ownership clusters is to provide access control to the datasets. For example, you can give users permission to access certain assets, findings, or both through the ownership clusters.
For JIT provisioning to work, you must create ownership clusters with the same name as your groups in Microsoft Entra ID, including case sensitivity. This way, as the users first log in to Brinqa, they are automatically added to the ownership clusters as members based on their group affiliation found in the SAML claim.
Users with the Configurator or System Administrator role can create or edit clusters. To create a new risk owner cluster, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Clusters and click Risk owners.
-
Click Create and fill in the following fields:
-
Name: Enter a name for the cluster. This name must match the group name in Microsoft Entra.
-
Description: Provide a description for the cluster.
-
Members: Leave it blank because users will be added automatically after their first login.
-
Conditions: Click + to add criteria for each data model. At the minimum, risk owners should have access to a set of hosts and vulnerabilities. For example:
-
Target data model: Click the dropdown and select Host.
ImportantAvoid selecting a parent data model (such as Asset, Finding, or Ticket) as the target. For example, instead of Asset, select a data model that extends Asset, such as Account, Host, Cloud Resource, and so on. This is because parent data models are not computed during consolidation and choosing a parent data model results in empty counts in the cluster.
-
Order: Specify the condition evaluation order for the target data model.
This field is important because it signifies the order that the Brinqa Platform follows to evaluate the conditions specified in this cluster and other clusters defined for the same dataset. The evaluation stops after a match is found, ensuring that each record is subject to only one ownership cluster. Therefore, it is logical to prioritize the most specific conditions first.
-
Condition: Specify the condition to define the hosts you want this cluster to view. The supported syntax is Brinqa Condition Language(BCL).
For example, if the
os CONTAINS "Windows"condition is met, users in this cluster can view hosts running the Windows operating system. -
Click Test condition to see the results retrieved by the condition. This ensures that your cluster groups the expected hosts.
-
-
Click + to add a condition for Vulnerability.
-
Target data model: Click the dropdown and select Vulnerability.
-
Order: Specify the condition evaluation order for the target data model.
-
Condition: Specify the condition to define the vulnerabilities you want this cluster to view.
For example, if the
targets.os CONTAINS "Windows"condition is met, users in this cluster can view vulnerabilities detected on machines running the Windows operating system. -
Click Test condition to see the results retrieved by the condition. This ensures that your cluster groups the expected vulnerabilities.
-
-
-
Click Create.
Clusters are synced through data computation. However, if you want the new clusters to go into effect immediately, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to Administration
> Data > Models.
-
Locate the data model that you have defined in the cluster. For example, Host or Vulnerability.
-
Click Flows.
-
Click the compute flow of your data model. For example, for the Host data model, click Host compute flow.
-
Click Launch, and then click Launch again in the confirmation dialog.
-
Repeat the steps for all the data models defined in your clusters.
-
Navigate to the Risk owner data model and click Flows.
-
Click Risk owner compute flow, then Launch, and then click Launch again in the confirmation dialog.
After the flows have run successfully, navigate to Clusters > Risk owners and click the cluster that you have created. Verify that the datasets defined by the conditions are viewable in the cluster. Alternatively, log in as a member of your clusters and verify that they can view the selected datasets.
If you see inaccurate or empty counts in the cluster, see the Troubleshooting section for information about potential causes of the issue.