Data Backup Policies
This article describes how Brinqa backs up your data, ensuring that your valuable information remains safe and accessible.
Brinqa solution cloud architecture
Before diving into backup policies, let's first explore the architecture and components of Brinqa solution. The following diagram outlines how data flows into the Brinqa Platform, gets processed by the Cyber Risk app, and is then stored in one of two database types: Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) or Online Analytical Processing (OLAP):
-
OLTP: The primary data store that ingests and processes data through orchestration.
-
OLAP: Designed for delivering analytic datasets at speed and scale. The platform takes a complete snapshot of the data from OLTP and stores the results for use in analytics and dashboards.
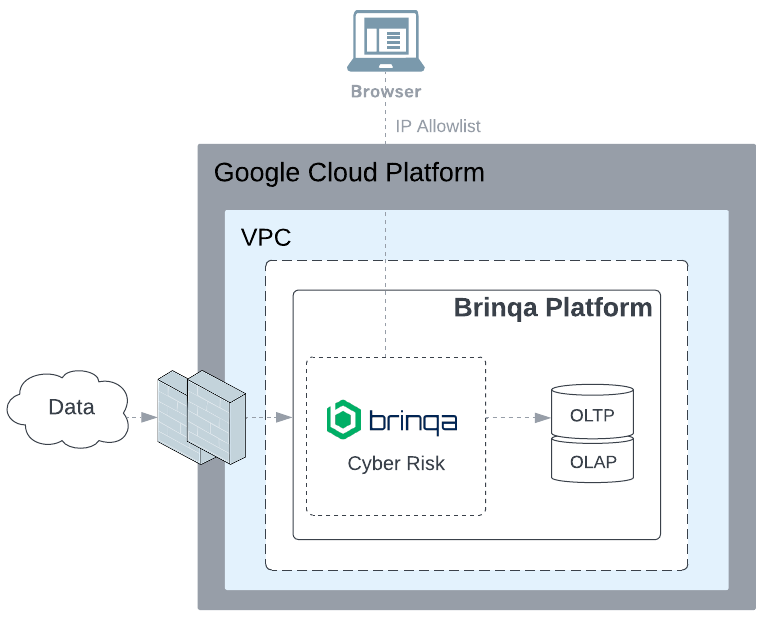
Figure 1. Brinqa solution cloud architecture diagram.
Brinqa Platform version 12 backup policies
If you are using Brinqa Platform version 12, refer to the backup policies in this section.
What data do we back up?
The primary data backup covers the transactional database, which serves as the OLTP database for the Brinqa Platform. The OLAP database is not backed up separately, as it is regenerated daily from the OLTP database as part of the Data Warehouse snapshot process. Off-site backups of the OLTP database are full backups.
The OLTP database is deployed in a distributed cluster architecture with servers spread across 3 availability zones for high availability. This distributed architecture differs significantly from version 11, which used a monolithic deployment with all components in a single virtual machine.
How are the backups configured?
The backup solution implements off-site backups for disaster recovery:
-
In-cluster snapshots with Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) capabilities will be available in a future release.
-
Off-site backups:
-
Purpose: Disaster recovery and long-term retention.
-
Frequency: Twice daily at 6:00 AM and 6:00 PM.
-
Performance: Backups typically complete in 4-5 minutes per database with minimal impact on production workloads.
-
Where are the backups stored?
Backups are stored in two different locations based on their type:
-
In-cluster snapshots: Will be available in a future release.
-
Off-site backups: Stored in Google Cloud Storage (GCS).
What is the retention period for all backup-related files?
The retention period differs based on the backup type:
-
In-cluster snapshots: Will be available in a future release.
-
Off-site backups: Retained for 30 days in GCS standard storage, then archived for an additional 90 days using tiered storage options.
What are the recovery objectives?
Brinqa's backup strategy is designed to meet specific recovery objectives:
-
Recovery Point Objective (RPO):
- Off-site backups: 12 hours maximum data loss (based on twice-daily backup schedule).
-
Recovery Time Objective (RTO):
- Full cluster recovery from off-site backups: 3-6 hours.
- PITR: Will be available in a future release.
Brinqa Platform version 11 backup policies
If you are using Brinqa Platform version 11, refer to the backup policies below.
What data do we back up?
When it comes to backups, it's important to know exactly what data is being protected. Here's a breakdown of the types of data being backed up and their frequency:
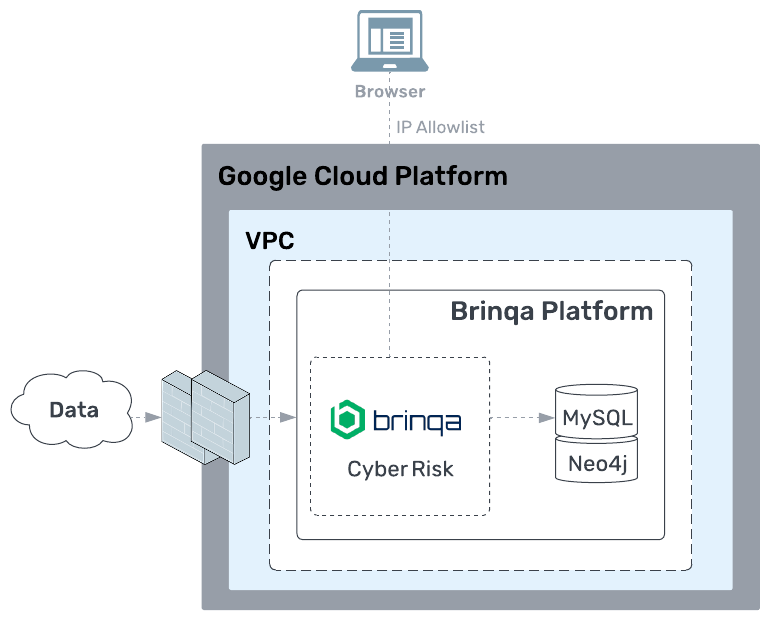
How are the backups configured?
Backing up data involves various methods and strategies to ensure that critical information is securely stored and can be easily restored when needed. Here's a detailed look at how data is backed up, including the tools and techniques:
-
Full system snapshots are initiated by a snapshot policy set in Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The policy is configured to run every hour and retain snapshots for one week.
-
MySQL data backup is managed through a script that is executed by
cron. -
Neo4j data backup is managed through a script that is executed by
cron.
Where are the backups stored?
Brinqa stores all backups in GCP Cloud Storage, which provides a reliable, secure, and scalable solution that aligns with our data management strategy.
What is the retention period for all backup-related files?
The retention period refers to the length of time that backup data is kept before it is deleted or overwritten. Different types of data and business needs dictate how long each type of backup is stored:
-
Full system snapshots are kept for seven days.
-
MySQL data backup is stored indefinitely.
-
Neo4j data backup is stored indefinitely.