Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a cloud environment solution that focuses on threat detection, assessments, and security management across your cloud environments. You can bring alert, alert definition, cloud resource, host, subscription, and security data from Microsoft Defender for Cloud into Brinqa to gain a comprehensive view of your cloud security landscape, thus enhancing your cybersecurity posture.
This document details the information you must provide for the connector to authenticate with Microsoft Defender for Cloud and how to obtain that information from Microsoft. See create a data integration for step-by-step instructions on setting up the integration.
Required connection settings
When setting up a data integration, select Microsoft Defender for Cloud from the Connector dropdown. If you cannot find the connector in the dropdown, make sure that you have installed it first. You must provide the following information to authenticate Microsoft Defender for Cloud with Brinqa:
-
API URL: The Microsoft Defender for Cloud API URL. The default URL is
https://management.azure.com. -
Login URL: The Microsoft Azure authentication URL. The default URL is
https://login.microsoftonline.com. -
Client ID and Client secret: The client ID and client secret associated with the service principal, which must have permissions to log in to the Microsoft Azure Active Directory (Active AD) and return data from the Azure REST API.
-
Tenant ID: The unique identifier for the Active AD tenant associated with the service principal.
Register a Microsoft Azure application
You must create a new application for the Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector to authenticate with Azure AD and access the Azure REST API. To register an application in your Azure AD tenant, follow these steps:
-
Log in to your Microsoft Azure Portal as an administrator.
-
Navigate to and click Microsoft Entra ID.
-
On the left-hand side of the page, click App registrations, and then click New registration.
-
Give your new application a name, select the supported account types, and provide an optional Redirect URI. If you do not have a redirect URI, you can leave the field as is.
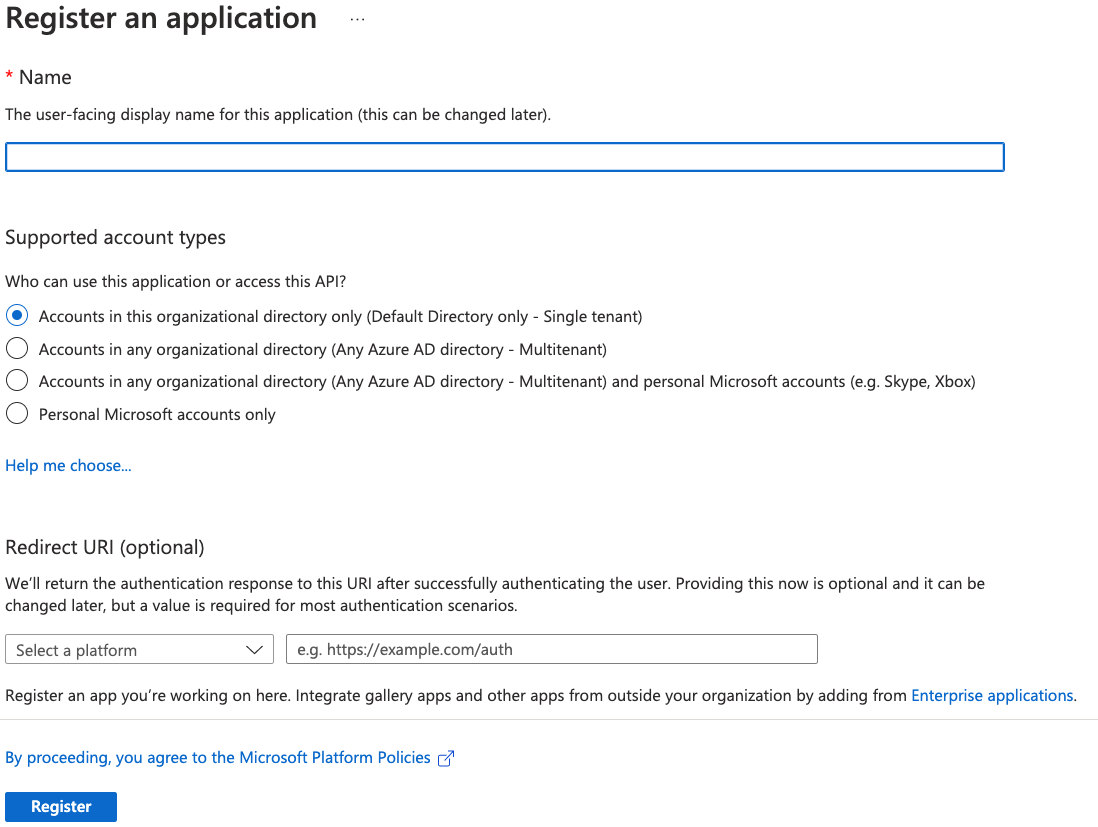
-
Click Register.
For additional details about registering an application in Azure AD and creating a service principal, see Microsoft Azure documentation.
Obtain Microsoft Azure credentials
After you have created your new Microsoft Azure application, your client and tenant ID display. Copy the Application (client) ID and Directory (tenant) ID as shown below:
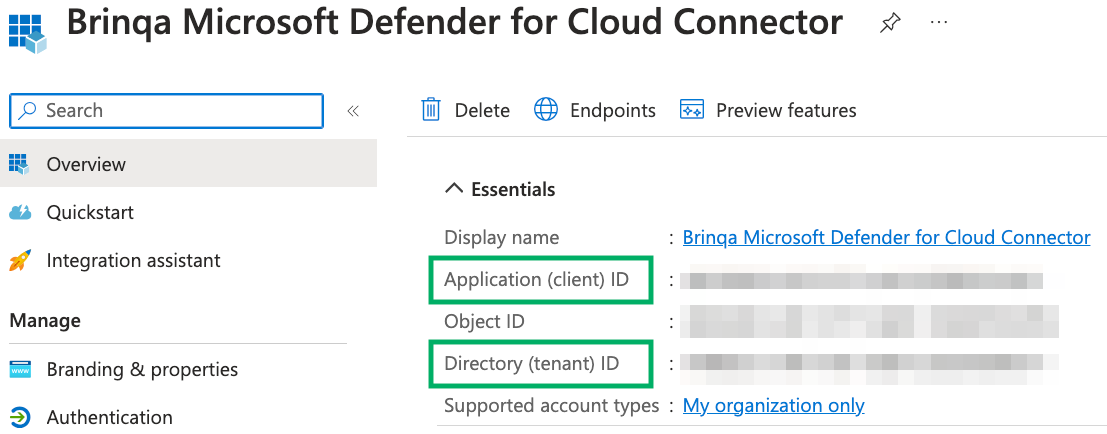
To obtain your client secret and optional subscription ID, follow these steps:
-
Click Certificates & secrets and then click New client secret.
-
Provide a description, set an expiry date, and then click Add.
The new client secret displays. You cannot view the client secret again. There is both a Value and Secret ID. The Value field is needed for authentication. Copy the Value field and save it to a secure location.
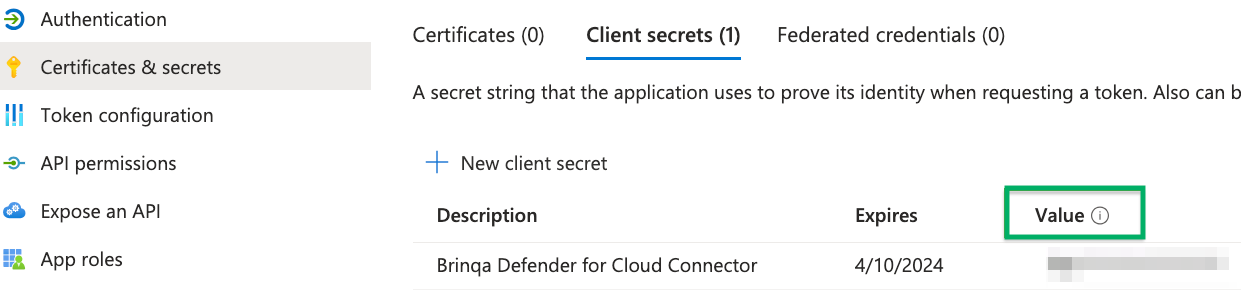
For additional details about obtaining your Microsoft Azure credentials, see Microsoft documentation.
Assign permissions
After you have created your new Microsoft Azure application and obtained the authentication credentials, you must assign the required permissions for the application to access your data. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Navigate to the applicable Azure subscription.
-
Click Access control (IAM), click Add, and then click Add role assignment from the dropdown.
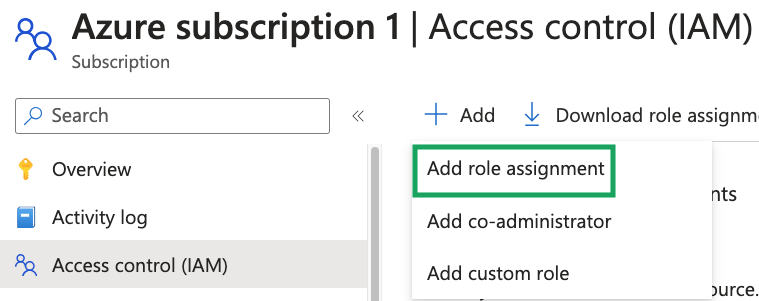
-
In the Job function roles tab, search for and select the Reader role.
- The Reader role allows you to view all resources, but does not grant permission to modify them.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Members tab, click the User, group, or service principal option.
-
Click Select members, search for and click the application you registered earlier, and then click Select.
-
Navigate to the Review + assign tab and click Review + assign.
If you do not have permissions to assign roles, contact your Azure administrator. For additional information, see Microsoft documentation.
(Optional) Create a management group for multiple subscriptions
If you have multiple Azure subscriptions, you can organize them into a single management group to uniformly set access controls. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Log in to your Microsoft Azure Portal as an administrator.
-
Search for "Management groups" in the search box and click Management groups.
-
Click Create, provide a management group ID and display name, and then click Submit.
-
On the Management groups page, click the name of the new management group.
-
Click Add subscription, select the Azure subscriptions you want to add to the management group, and then click Save.
-
Click Access control (IAM), click Add, and then click Add role assignment from the dropdown.
-
Search for and select the role you want to assign to the management group.
-
Click Next.
-
In the Members tab, click the User, group, or service principal option.
-
Click Select members, search for and click the application you registered earlier, or any relevant members who require this role, and then click Select.
-
Navigate to the Review + assign tab and click Review + assign.
If you do not have permissions to create management groups, contact your Azure administrator. For additional information, see Microsoft documentation.
Additional settings
The Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector contains additional options for specific configuration:
-
Maximum retries: The maximum number of times that the integration attempts to connect to the Azure REST API before giving up and reporting a failure. The default setting is 5.
-
Subscription ID: A comma-separated list of unique identifiers for your Microsoft Azure subscriptions, which represent billing and resource usage entities within Azure. If no subscription IDs are provided, the connector retrieves data from all subscriptions associated with the tenant. To obtain your subscription ID, follow these steps:
-
Log in to your organization's Microsoft Azure Portal as an administrator.
-
Search for "Subscriptions" in the search box at the top of the page and click Subscriptions.
The subscription IDs for your corresponding applications display. If desired, copy these values into the Subscription ID field in the integration configuration.
Azure Subscription IDsOnly provide a Subscription ID if you want to retrieve resources from specific subscriptions. Leave this field blank to retrieve data from all subscriptions.
-
Types of data to retrieve
The Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector can retrieve the following types of data from the Azure REST API:
Table 1: Data retrieved from Azure REST API
| Connector Object | Required | Maps to Data Model |
|---|---|---|
| Alert | Yes | Alert |
| Alert Definition | Yes | Alert Definition |
| Assessment | Yes | Violation |
| Assessment Metadata | Yes | Violation Definition |
| Asset | Yes | Cloud Resource |
| Host | Yes | Host |
| Resource Group | No | Not mapped |
| Subscription | Yes | Cloud Resource |
| Vulnerability | Yes | Vulnerability |
| Vulnerability Definition | Yes | Vulnerability Definition |
The Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector does not currently support operation options for the types of data it retrieves.
For detailed steps on how to view the data retrieved from Microsoft Defender for Cloud in the Brinqa Platform, see How to view your data.
Attribute mappings
Expand the sections below to view the mappings between the source and the Brinqa data model attributes.
Alert
Table 2: Alert attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| actionTaken | Local variable |
| additionalData | Local variable |
| associatedResource | targets |
| canBeInvestigated | Local variable |
| compromisedEntity | Local variable |
| confidenceReasons | Local variable |
| description | type |
| endTime | sourceLastModified |
| instanceId | Local variable |
| isIncident | Local variable |
| name | Local variable |
| processingTime | Local variable |
| startTime | sourceCreatedDate |
| state | status, statusCategory |
| subscriptionId | targets |
| sysId | uid |
| title | Local variable |
| workspaceArmId | Local variable |
Alert Definition
Table 3: Alert Definition attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| actionTaken | Local variable |
| canBeInvestigated | Local variable |
| compromisedEntity | Local variable |
| confidenceReasons | Local variable |
| description | description |
| instanceId | Local variable |
| isIncident | Local variable |
| name | Local variable |
| processingTime | Local variable |
| remediation | remediation |
| reportedSeverity | severity, sourceSeverity |
| title | uid, name |
| vendorName | affected |
| workspaceArmId | Local variable |
Assessment
Table 4: Assessment attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| sysId | uid |
| subscriptionId | Local variable |
| metadataName | Local variable |
| resourceId | targets, Local variable |
| title | name |
| statusCode | status |
| STATUS_CAUSE | Local variable |
| STATUS_DESCRIPTION | Local variable |
| TARGET | targets |
| TYPE | type |
Assessment Metadata
Table 5: Assessment Metadata attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| ASSESSMENT_TYPE | categories |
| CATEGORIES | categories |
| DESCRIPTION | description |
| IMPLEMENTATION_EFFORT | Local variable |
| NAME | name |
| POLICY_ID | Local variable |
| PREVIEW | Local variable |
| REMEDIATION | remediation |
| SEVERITY | severity, sourceSeverity, severityScore |
| SYS_ID | uid |
| THREATS | Local variable |
| TITLE | Local variable |
| USER_IMPACT | Local variable |
| PROVIDER_ID | Local variable |
Asset
Table 6: Asset attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| SYS_ID | uid |
| RESOURCE_ID | description, Local variable |
| SUBSCRIPTION_ID | description, Local variable |
| RESOURCE_NAME | description, name |
| RESOURCE_TYPE | categories, Local variable |
| SKU_NAME | Local variable |
| SKU_CAPACITY | Local variable |
| SKU_FAMILY | Local variable |
| SKU_MODEL | Local variable |
| SKU_SIZE | Local variable |
| SKU_TIER | Local variable |
| KIND | Local variable |
| LOCATION | Local variable |
| IDENTITY_PRINCIPAL_ID | Local variable |
| IDENTITY_TENANT_ID | Local variable |
| IDENTITY_TYPE | Local variable |
| PLAN_NAME | Local variable |
| PLAN_PRODUCT | Local variable |
| PLAN_VERSION | Local variable |
| CREATED_TIME | sourceCreatedDate |
| CHANGED_TIME | sourceLastModified |
| PROVISIONING_STATE | status |
| TAGS | tags |
Host
Table 7: Host attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| CHANGED_TIME | sourceModifiedDate |
| CREATED_TIME | sourceCreatedDate |
| IDENTITY_PRINCIPAL_ID | Local variable |
| IDENTITY_TENANT_ID | Local variable |
| IDENTITY_TYPE | Local variable |
| KIND | Local variable |
| LOCATION | Local variable |
| PLAN_NAME | Local variable |
| PLAN_PRODUCT | Local variable |
| PLAN_PUBLISHER | Local variable |
| PLAN_VERSION | Local variable |
| PROVISIONING_STATE | status(normalized), sourceStatus |
| RESOURCE_ID | description |
| RESOURCE_NAME | description, hostnames, name |
| RESOURCE_TYPE | categories |
| SKU_CAPACITY | Local variable |
| SKU_FAMILY | Local variable |
| SKU_MODEL | Local variable |
| SKU_NAME | Local variable |
| SKU_SIZE | Local variable |
| SKU_TIER | Local variable |
| SUBSCRIPTION_ID | description |
| SYS_ID | uid |
| TAGS | tags |
Subscription
Table 8: Subscription attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| ASSET_CATEGORY_CLOUD_RESOURCE | categories |
| DISPLAY_NAME | name |
| STATE | status(normalized),sourceStatus |
| TAGS | tags |
| UID | uid |
Vulnerability
Table 9: Vulnerability attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| CATEGORIES | categories |
| ID | uid |
| PATCHABLE | Local variable |
| RESOURCE_GROUP | Local variable |
| RESOURCE_ID | Local variable |
| SOFTWARE_INSTALLED_VERSION | Local variable |
| STATUS | status(normalized), statusCategory, sourceStatus |
| STATUS_CAUSE | Local variable |
| STATUS_DESCRIPTION | Local variable |
| SUBSCRIPTION_ID | Local variable |
| TARGETS | targets |
| TIME_GENERATED | firstFound |
| UID | type, uid |
| VULNERABILITY_TYPE | type |
Vulnerability Definition
Table 10: Vulnerability Definition attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| CATEGORIES | categories |
| CVE_IDS | cveIds, cveRecords |
| DESCRIPTION | description |
| DISPLAY_NAME | summary |
| NAME | name |
| REMEDIATION | recommendation |
| SEVERITY | severity |
| UID | type, uid |
| SOURCE_SEVERITY | severity, sourceSeverity |
| SEVERITY_SCORE | severityScore |
Local variable indicates that the field is processed within a specific context, such as a particular workflow or calculation. Unlike other attributes, local variables aren't mapped to the unified data models. They only exist on the source data model.
APIs
The Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector uses the Azure REST API. Specifically, it uses the following endpoints:
Table 11: Microsoft Defender for Cloud API Endpoints
| Connector Object | API Endpoints |
|---|---|
| Alert | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/providers/Microsoft.Security/alerts |
| Alert Definition | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/providers/Microsoft.Security/alerts |
| Assessment | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/providers/Microsoft.Security/assessments |
| Assessment Metadata | GET /providers/Microsoft.Security/assessmentMetadata |
| Asset | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resources |
| Host | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resources |
| Resource Group | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/resourcegroups |
| Subscription | - GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID} (Used when subscription IDs are provided) - GET /subscriptions (Used when no subscriptions IDs are provided to retrieve all subscriptions) |
| Vulnerability | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/providers/Microsoft.Security/subAssessments |
| Vulnerability Definition | GET /subscriptions/{subscriptionID}/providers/Microsoft.Security/subAssessments |
The assessments endpoint creates Violations and subAssessements endpoint creates Vulnerabilities
Changelog
The Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector has undergone the following changes:
This connector is part of a bundled release with other connectors from the same vendor. If a version shows "No change", it means that the connector version was updated for consistency as part of the bundle, but no functional changes were made to this specific connector. You can update to or skip this version without affecting your existing configuration.
Table 12: Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector changelog
| Version | Description | Date Published |
|---|---|---|
| 3.4.28 | The connector now maps SubAssessment objects without CVEs to the Violation and Violation Definition objects, expanding the scope of findings retrieved. | February 4th, 2026 |
| 3.4.27 | No change. | January 26th, 2026 |
| 3.4.26 | Enhanced to properly extract and map AWS cloud resource data to violations and vulnerabilities. | November 17th, 2025 |
| 3.4.25 | Added a LAST_CAPTURED attribute to both Host and Vulnerability objects. | November 17th, 2025 |
| 3.4.24 | No change. | November 10th, 2025 |
| 3.4.23 | No change. | October 23rd, 2025 |
| 3.4.22 | Added mapping of Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources to the TARGET attribute in the Violation object. | October 16th, 2025 |
| 3.4.21 | No change. | October 15th, 2025 |
| 3.4.20 | No change. | September 17th, 2025 |
| 3.4.19 | No change. | August 5th, 2025 |
| 3.4.18 | No change. | August 4th, 2025 |
| 3.4.17 | No change. | August 1st, 2025 |
| 3.4.16 | Normalized the TARGETS attribute on the Vulnerability and Violation objects and the UID attribute on the Cloud Resource and Host objects to lowercase to ensure vulnerabilities and violations correctly link to their associated assets. This resolves an issue where casing mismatches were preventing proper relationships. | June 11th, 2025 |
| 3.4.15 | No change. | May 27th, 2025 |
| 3.4.14 | Fixed an issue where the connector sync was failing with a "status":500 error. | May 21st, 2025 |
| 3.4.13 | - Fixed an issue where Vulnerability Definitions were missing CVSS scores despite the data being available in Microsoft Defender for Cloud. - Fixed data type mismatch errors on the Vulnerability Definition object for the PUBLISHED_DATE and SOURCE_LAST_MODIFIED attributes. | May 20th, 2025 |
| 3.4.12 | Fixed an issue where CVE identifiers were not correctly mapped on the Vulnerability Definition object, resulting in missing CVE IDs and CVE Records. The connector now populates CVE metrics wherever CVSS metrics are available. | April 22nd, 2025 |
| 3.4.11 | Renamed the PATCH_AVAILABLE attribute to PATCHABLE on the Vulnerability Definition object. | April 7th, 2025 |
| 3.4.10 | No change. | April 1st, 2025 |
| 3.4.9 | No change. | March 26th, 2025 |
| 3.4.8 | Fixed an issue where the connector was not retrieving all vulnerabilities from Microsoft. | February 12th, 2025 |
| 3.4.7 | Enhanced the connector to not retrieve compliance-type findings from Microsoft, as these are classified as recommendations rather than vulnerabilities. As a result, the CATEGORIES and VULNERABILITY_TYPE attributes were added to the Vulnerability object. | January 28th, 2025 |
| 3.4.5 | No change. | December 19th, 2024 |
| 3.4.4 | Code cleanup and general maintenance. | December 6th, 2024 |
| 3.4.3 | The connector now retrieves the Resource Group object from Microsoft. | November 28th, 2024 |
| 3.4.2 | - Fixed an issue where asset names overlapped between different subscriptions. The connector now uses resource IDs to uniquely identify assets. - Normalized UIDs to resolve consolidation issues between violations and vulnerabilities. | October 7th, 2024 |
| 3.4.1 | No change. | September 27th, 2024 |
| 3.4.0 | - Made the Subscription ID optional in the integration configuration. If no subscription IDs are provided, the connector retrieves all available subscriptions for the provided tenant. Before updating to version 3.4.0, ensure that if you do not specify any subscription IDs, the connector retrieves data from all subscriptions. This may result in more data being brought in than expected. Specify subscription IDs if you want to limit data retrieval to only specific subscriptions. - The default status attribute value for the Cloud Resource and Host objects are set to "Active". | September 17th, 2024 |
| 3.3.10 | Code cleanup and general maintenance. | September 4th, 2024 |
| 3.3.9 | Fixed an issue where the Microsoft Defender for Cloud connector threw a "NoClassDefFound" error when updating the data integration to version 3.3.8. | August 27th, 2024 |
| 3.3.8 | No change. | July 24th, 2024 |
| 3.3.7 | No change. | July 24th, 2024 |
| 3.3.6 | No change. | July 8th, 2024 |
| 3.3.5 | No change. | May 20th, 2024 |
| 3.3.4 | - Made the TARGETS attribute lowercase on the Violation and Vulnerability objects. - Made the UID attribute lowercase on the Asset object. | May 20th, 2024 |
| 3.3.3 | No change. | May 20th, 2024 |
| 3.3.2 | No change. | May 9th, 2024 |
| 3.3.1 | No change. | May 3rd, 2024 |
| 3.3.0 | No change. | April 30th, 2024 |
| 3.2.2 | No change. | April 26th, 2024 |
| 3.2.1 | No change. | April 19th, 2024 |
| 3.2.0 | No change. | April 4th, 2024 |
| 3.1.18 | No change. | April 4th, 2024 |
| 3.1.17 | No change. | March 24th, 2024 |
| 3.1.16 | No change. | March 14th, 2024 |
| 3.1.15 | No change. | February 11th, 2024 |
| 3.1.14 | No change. | February 2nd, 2024 |
| 3.1.13 | No change. | January 26th, 2024 |
| 3.1.12 | - The connector now maps the Assessment object to the Violation data model. - The connector now maps the Assessment Metadata object to the Violation Definition data model. | January 24th, 2024 |
| 3.1.11 | Initial Integration+ release. | October 11th, 2023 |