Fleet
Fleet is an open-source asset management tool that monitors and scans your hosts and software inventory for potential vulnerabilities. You can bring host, software, and security data from Fleet into Brinqa to form a unified view of your asset inventory and attack surface, thus strengthening your cybersecurity posture.
This document details the information you must provide for the connector to authenticate with Fleet and how to obtain that information from Fleet. See create a data integration for step-by-step instructions on setting up the integration.
Required connection settings
When setting up a data integration, select Fleet from the Connector dropdown. You must provide the following information to authenticate Fleet with Brinqa:
-
API URL: The Fleet API Server URL.
-
API token: The API token associated with the Fleet account, which must have permissions to log in to the API server and return data.
Generate a Fleet API token
For the Fleet connector to retrieve data from the Fleet REST API, you must provide an API token. To do so, follow these steps:
-
Log in to your organization's Fleet account as an administrator.
-
Click the profile photo and then click My account from the dropdown.
-
Click Get API token.
Your new API token displays. You can not view the token again after this. Copy and save it to a secure location.
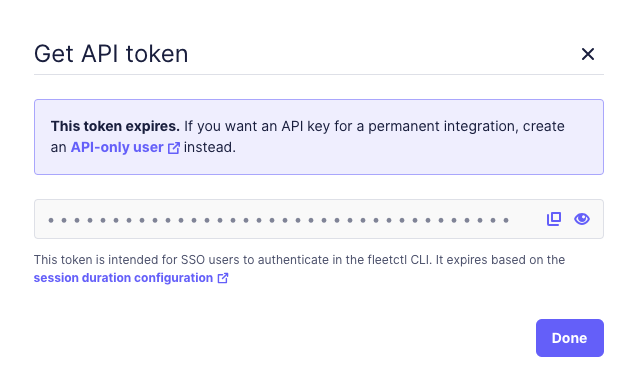
-
Click Done.
While any user can create API tokens to retrieve data from the Fleet API, Fleet recommends creating an API-only user, as tokens for regular users frequently expire, which can cause disruptions in your workflows. Additionally, the API-only user is assigned the Observer role by default, which is the minimum role required for API access. Fleet Premium customers can also assign team-level access for stricter access. For additional information, see Fleet documentation.
If you do not have permissions to create an API token, contact your Fleet administrator. For additional information, see Fleet documentation.
Additional settings
The Fleet connector contains additional options for specific configuration:
-
Page size: The maximum number of records to get per API request. The default setting is 100. It is not recommended to go over 100.
-
Parallel requests: The maximum number of parallel API requests. The default setting is 4.
-
Maximum retries: The maximum number of times that the integration attempts to connect to the Fleet API before giving up and reporting a failure. The default setting is 5.
-
Requests per minute: The maximum number of API requests per minute. The default setting is 1800. You can enter 0 to disable rate limiting.
Types of data to retrieve
The Fleet connector can retrieve the following types of data from the Fleet REST API:
Table 1: Data retrieved from Fleet
| Connector Object | Required | Maps to Data Model |
|---|---|---|
| Host | Yes | Host |
| Installed Package | Yes | Installed Package |
| Package | Yes | Package |
| Vulnerability | Yes | Vulnerability |
| Vulnerability Definition | Yes | Vulnerability Definition |
The Fleet connector does not currently support operation options for the types of data it retrieves.
For detailed steps on how to view the data retrieved from Fleet in the Brinqa Platform, see How to view your data.
Attribute mappings
Expand the sections below to view the mappings between the source and the Brinqa data model attributes.
Host
Table 2: Host attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| build | Local variable |
| code_name | Local variable |
| computer_name | Local variable |
| config_tls_refresh | Local variable |
| cpu_brand | Local variable |
| cpu_logical_cores | Local variable |
| cpu_physical_cores | Local variable |
| cpu_subtype | Local variable |
| cpu_type | Local variable |
| created_at | sourceCreatedDate |
| detail_updated_at | Local variable |
| distributed_interval | Local variable |
| display_name | Local variable |
| display_text | Local variable |
| encryption_key_available | Local variable |
| enrollment_status (mdm) | Local variable |
| failing_policies_count (issues) | Local variable |
| gigs_disk_space_available | Local variable |
| hardware_model | Local variable |
| hardware_serial | serialNumber |
| hardware_vendor | Local variable |
| hardware_version | Local variable |
| hostname | hostnames |
| id | uid |
| label_updated_at | Local variable |
| last_enrolled_at | Local variable |
| logger_tls_period | Local variable |
| memory | Local variable |
| name (mdm) | Local variable |
| os_version | operatingSystem |
| osquery_version | Local variable |
| pack_stats | Local variable |
| percent_disk_space_available | Local variable |
| platform | Local variable |
| platform_like | Local variable |
| policy_updated_at | Local variable |
| primary_ip | ipAddresses |
| primary_mac | macAddresses |
| public_ip | publicIpAddresses |
| refetch_critical_queries_until | Local variable |
| refetch_requested | Local variable |
| server_url (mdm) | Local variable |
| seen_time | lastSeen |
| software_updated_at | Local variable |
| status | status |
| team_id | Local variable |
| team_name | Local variable |
| total_issues_count (issues) | Local variable |
| updated_at | sourceLastModified |
| uptime | Local variable |
| uuid | Local variable |
Local variable indicates that the field is processed within a specific context, such as a particular workflow or calculation. Unlike other attributes, local variables aren't mapped to the unified data models. They only exist on the source data model.
Installed Package
Table 3: Installed Package attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| bundleIdentifier | Local variable |
| cve (vulnerabilities) | cveIds |
| details_link (vulnerabilities) | Local variable |
| generated_cpe | affected |
| host.id | targets |
| id | uid, type |
| installedPaths | Local variable |
| name | name |
| source | Local variable |
| version | currentVersion |
Local variable indicates that the field is processed within a specific context, such as a particular workflow or calculation. Unlike other attributes, local variables aren't mapped to the unified data models. They only exist on the source data model.
Package
Table 4: Package attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| arch | Local variable |
| cve (vulnerabilities) | Local variable |
| details_link (vulnerabilities) | Local variable |
| generated_cpe | cpeIds |
| hosts_count | Local variable |
| id | uid |
| name | name |
| release | Local variable |
| source | Local variable |
| vendor | Local variable |
| version | currentVersion |
Local variable indicates that the field is processed within a specific context, such as a particular workflow or calculation. Unlike other attributes, local variables aren't mapped to the unified data models. They only exist on the source data model.
Vulnerability
Table 5: Vulnerability attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| id | uid |
| status | status, sourceStatus, statusCategory |
| target | targets |
| vulnerability.cve | type |
Local variable indicates that the field is processed within a specific context, such as a particular workflow or calculation. Unlike other attributes, local variables aren't mapped to the unified data models. They only exist on the source data model.
Vulnerability Definition
Table 6: Vulnerability Definition attribute mappings
| Source Field Name | Maps to Attribute |
|---|---|
| cve | cveIds, cveRecords, name, uid |
| detailsLink | description, references |
Local variable indicates that the field is processed within a specific context, such as a particular workflow or calculation. Unlike other attributes, local variables aren't mapped to the unified data models. They only exist on the source data model.
Operation options
The Fleet connector supports the following operation options. See connector operation options for information about how to apply them.
Table 7: Fleet connector operation options
| Connector Object | Option | All Possible Values | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All connector objects | PAGE_SIZE | Any numeric value | Specify the maximum number of records to retrieve per API request for the specified connector object. It is not recommended to go over 100. | Key: PAGE_SIZE Value: 50. This key and value combination retrieves up to 50 records per request for the specified connector object. |
| PARALLELISM_LEVEL | Any numeric value | Specify the maximum number of parallel API requests for the specified connector object. | Key: PARALLELISM_LEVEL Value: 2. This key and value combination limits parallel API requests to 2 for the specified connector object. |
The option keys and values are case-sensitive as they are shown in this documentation.
APIs
The Fleet connector uses the Fleet REST API v1. Specifically, it uses the following endpoints:
Table 8: Fleet REST API Endpoints
| Connector Object | API Endpoint |
|---|---|
| Host | GET /api/v1/fleet/hosts |
| Installed Package | GET /api/v1/fleet/hosts GET /api/v1/fleet/hosts/{Id} |
| Package | GET /api/v1/fleet/software |
| Vulnerability | GET /api/v1/fleet/hosts GET /api/v1/fleet/hosts/{Id} |
| Vulnerability Definition | GET /api/v1/fleet/hosts GET /api/v1/fleet/hosts/{Id} |
Changelog
The Fleet connector has undergone the following changes:
Table 9: Fleet connector changelog
| Version | Description | Date Published |
|---|---|---|
| 3.1.4 | Added a check for null and isNotBlank for the UUID attribute in the Host object. | October 10th, 2025 |
| 3.1.3 | Added operation options to help manage and optimize API call handling: PAGE_SIZE and PARALLELISM_LEVEL. | September 18th, 2024 |
| 3.1.2 | Code cleanup and maintenance. | September 18th, 2024 |
| 3.1.1 | Added the FIXED_VERSION attribute to the Vulnerability Definition object. | September 16th, 2024 |
| 3.1.0 | - Added two new additional settings to help manage API throttling and optimize API call handling: Maximum retries and Requests per minute. - Enhanced how the Fleet connector generates UIDs. | September 16th, 2024 |
| 3.0.0 | Initial Integration+ release. | May 3rd, 2024 |