Write BQL with Natural Language
BrinqaIQ offers a BQL Query Builder that can convert your natural language questions or prompts into valid Brinqa Query Language (BQL) queries, enabling you to quickly locate relevant information and get answers to your questions.
For additional information about how BrinqaIQ works, data usage, and safeguards, see the BrinqaIQ Overview.
Use BrinqaIQ to generate BQL queries
To search for information in the Brinqa Platform ,such as assets, findings, or other data types, but without extensive knowledge of BQL, you can simply type your question into the chatbot. BrinqaIQ responds with a suggested BQL query, which you can review and edit before running.
For example, you might say: “I need all vulnerabilities discovered in the last month or 30 days,” and BrinqaIQ may respond with:
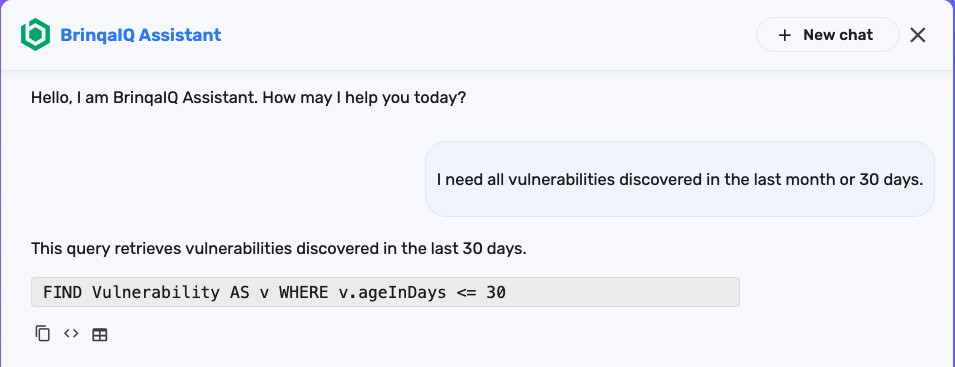
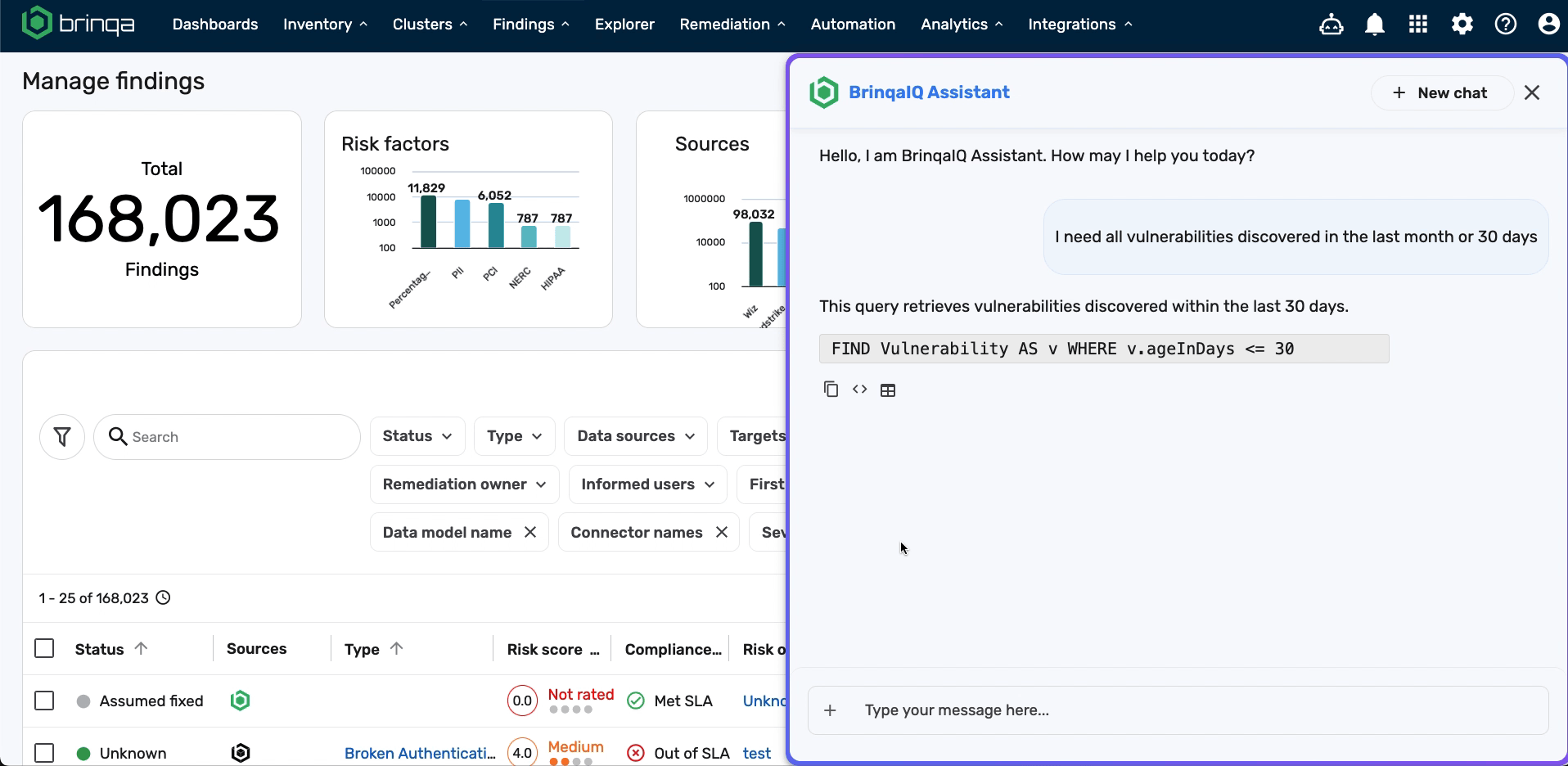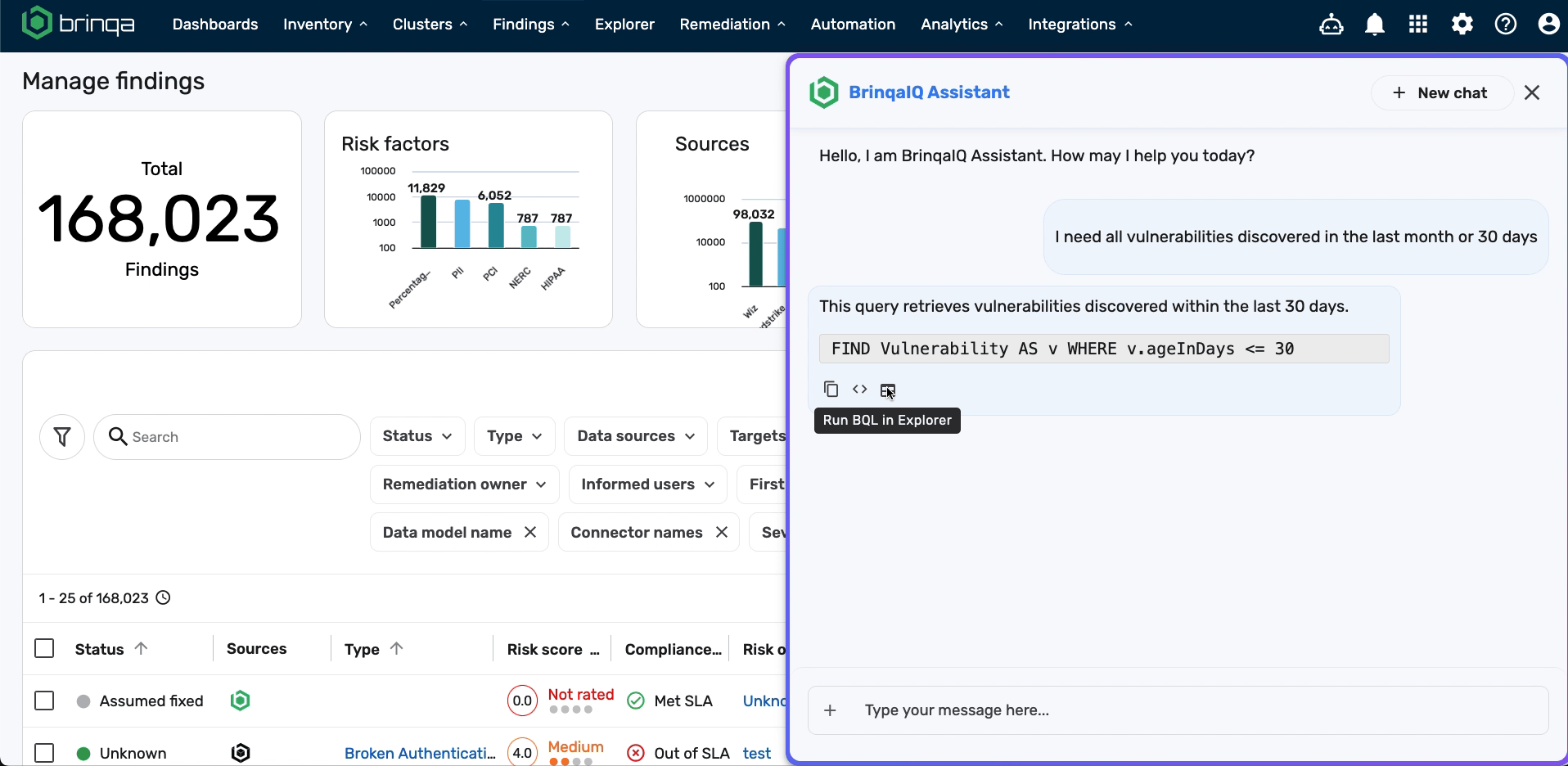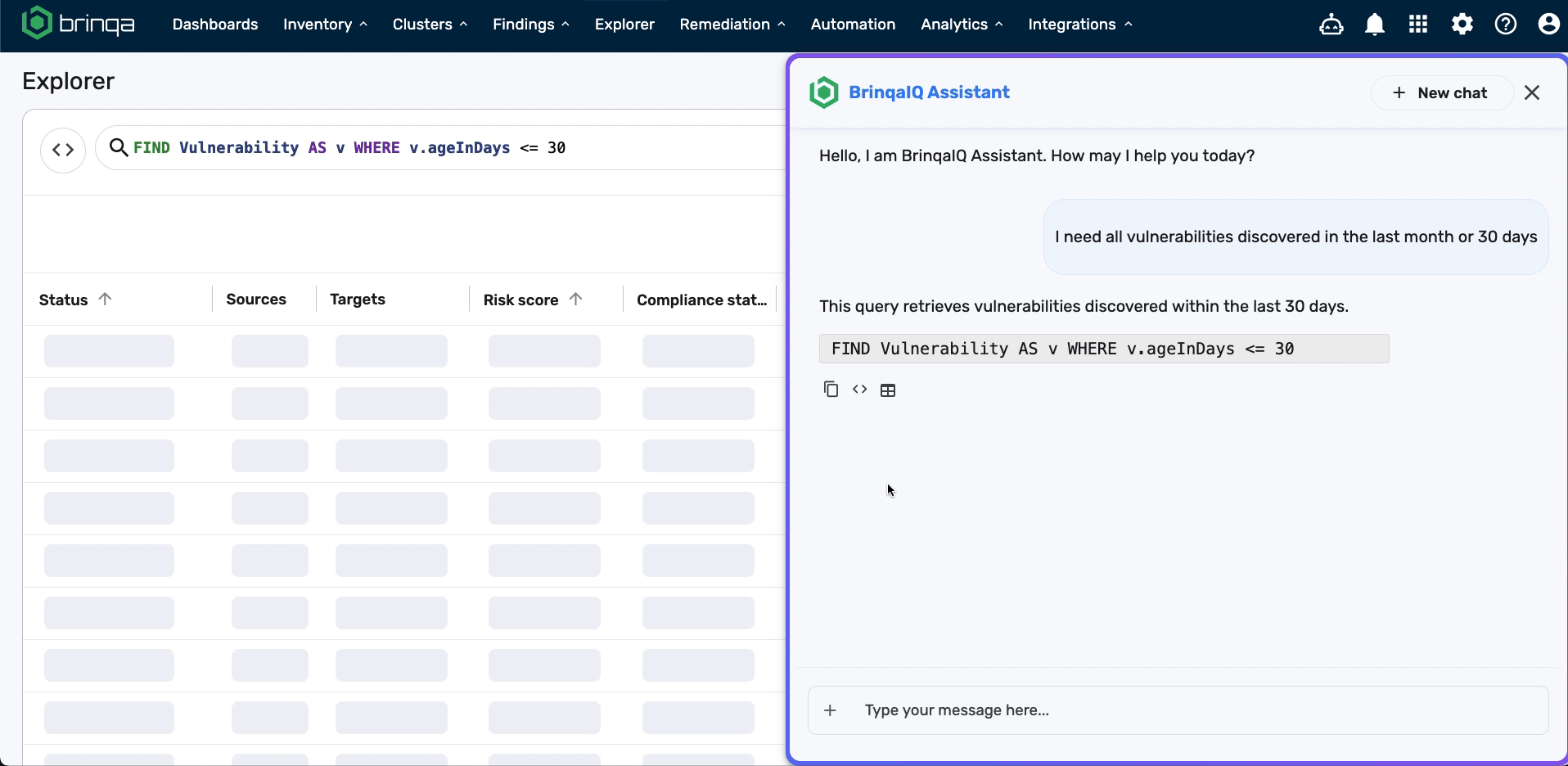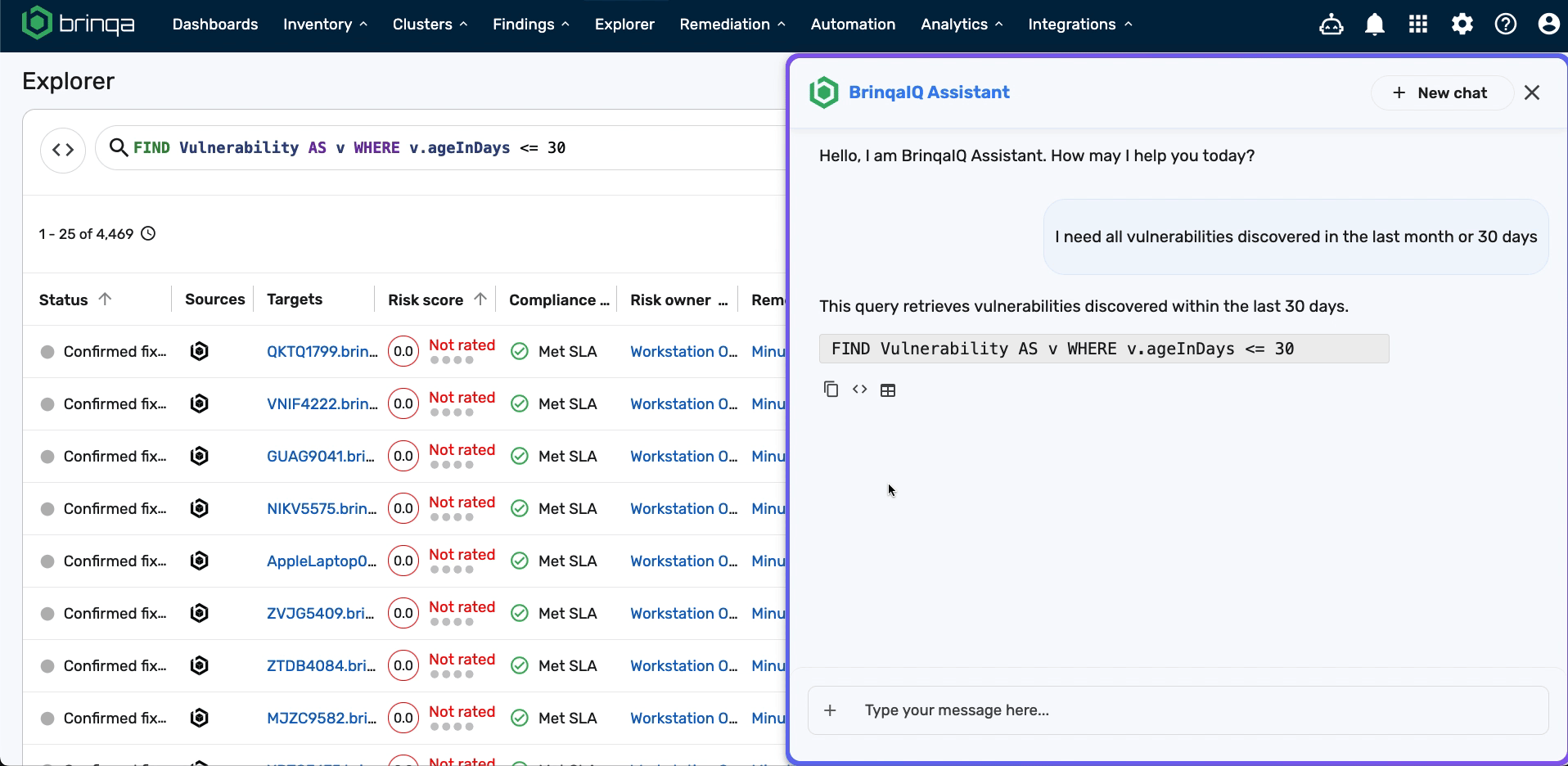
When BrinqaIQ responds with a BQL query, you’ll see three buttons below the response:
-
Copy response to clipboard
: Copies the full chatbot response, including the explanation and the BQL query.
-
Copy code to clipboard
: Copies only the BQL query to your clipboard.
-
Run BQL in Explorer
: Opens the Explorer page and runs the query.
Example prompts
Here are some examples to help you get started with using natural language to generate BQL queries:
- Show me all findings discovered in the last 7 days
- List critical findings on confirmed active assets
- What assets have more than 5 open findings?
- Give me all findings on assets tagged with 'PCI'
- Which vulnerabilities were fixed in the last 30 days?
Current limitations
While BrinqaIQ can translate many natural language prompts into valid BQL queries, there are some known limitations to be aware of:
-
Overuse of relationships: BrinqaIQ may emphasize relationships more than necessary. For example, when asking "Show me all vulnerabilities from the past 30 days," BrinqaIQ might generate a query that includes a
THAT HASclause to relate vulnerabilities to assets, even though it's not needed to answer the prompt. -
Incorrect condition values: Sometimes, the generated query includes a value that isn’t valid for the specified attribute. For instance, if you ask about confirmed active assets, it may use
a.status = "active"instead of the correct value like"Confirmed active". -
Sorting: BrinqaIQ does not currently support generating BQL queries that use sorting operations like
ORDER BY. To be specific, even if you ask for "top 10 vulnerabilities by risk score," the returned query won’t include anORDER BY riskScore DESCclause. -
Keyword limitations: The following BQL keywords are not yet supported in BrinqaIQ:
DISTINCTOPTIONALLYWITH
-
Operator limitations: The following BQL operators are supported in BrinqaIQ:
BEFORE/SINCECONTAINS/CONTAINS ANY/NOT CONTAINSEQUALS TO(=)/NOT EQUALS TO(!=)EXISTS/NOT EXISTSGREATER THAN(>)/GREATER THAN OR EQUAL TO(>=)IN/IN LAST/IN NEXTIS DATE/IS NOT DATEIS NULL/IS NOT NULLLESS THAN(<)/LESS THAN OR EQUAL TO(<=)LIKE/NOT LIKENOT IN/NOT IN LAST/NOT IN NEXTSTARTS WITH/ENDS WITH
Brinqa is actively working to expand the range of supported keywords, operators, and improve how BrinqaIQ interprets and generates BQL queries. Future updates will address these limitations and add support for more advanced queries.
Query validity
BrinqaIQ interprets your natural language questions and generates a BQL query using metadata from the Brinqa Platform and BQL documentation. To ensure accurate results, Brinqa advises that you keep your questions specific and clearly scoped. For example, “What are all critical findings discovered in the last week on active assets?” is easier to interpret than a broad prompt like “Give me a security summary,” which is too vague and may not return the results you expect.
If your question is vague or includes multiple unrelated ideas, BrinqaIQ may misinterpret your intent. You can refine your prompt in a follow-up message or edit the generated query before running it.